你好,我是孔令飞。
上节课,我介绍了 kube-scheduler 在启动时,需要加载的调度插件和调度策略,可以理解为 kube-scheduler 的静态部分。接下来要介绍的调度队列管理、调度 Pod 流程是 kube-scheduler 的动态部分,是调度器的最核心逻辑。
调度队列管理
kube-scheduler 会从调度队列中获取需要调度的 Pod 和目标 Node 列表,通过调度流程,最终将 Pod 调度到合适的 Node 节点上。
创建调度队列
我们先来看下调度队列是如何创建的。
在 scheduler.New 中,通过以下代码创建了优先级调度队列 podQueue:
func New(ctx context.Context,
client clientset.Interface,
informerFactory informers.SharedInformerFactory,
dynInformerFactory dynamicinformer.DynamicSharedInformerFactory,
recorderFactory profile.RecorderFactory,
opts ...Option) (*Scheduler, error) {
...
// 首先遍历 profiles 获取其对应的已注册好的 PreEnqueuePlugins 插件,这些插件会在 Pods 被添加到 activeQ 之前调用。
preEnqueuePluginMap := make(map[string][]framework.PreEnqueuePlugin)
queueingHintsPerProfile := make(internalqueue.QueueingHintMapPerProfile)
for profileName, profile := range profiles {
preEnqueuePluginMap[profileName] = profile.PreEnqueuePlugins()
queueingHintsPerProfile[profileName] = buildQueueingHintMap(profile.EnqueueExtensions())
}
// 初始化一个优先队列作为调度队列
podQueue := internalqueue.NewSchedulingQueue(
profiles[options.profiles[0].SchedulerName].QueueSortFunc(),
informerFactory,
// 设置 pod 的 Initial阶段的 Backoff 的持续时间
internalqueue.WithPodInitialBackoffDuration(time.Duration(options.podInitialBackoffSeconds)*time.Second),
// 最大backoff持续时间
internalqueue.WithPodMaxBackoffDuration(time.Duration(options.podMaxBackoffSeconds)*time.Second),
internalqueue.WithPodLister(podLister),
// 设置一个pod在 unschedulablePods 队列停留的最长时间
internalqueue.WithPodMaxInUnschedulablePodsDuration(options.podMaxInUnschedulablePodsDuration),
internalqueue.WithPreEnqueuePluginMap(preEnqueuePluginMap),
internalqueue.WithQueueingHintMapPerProfile(queueingHintsPerProfile),
// 指标相关
internalqueue.WithPluginMetricsSamplePercent(pluginMetricsSamplePercent),
internalqueue.WithMetricsRecorder(*metricsRecorder),
)
...
sched := &Scheduler{
Cache: schedulerCache,
client: client,
nodeInfoSnapshot: snapshot,
percentageOfNodesToScore: options.percentageOfNodesToScore,
Extenders: extenders,
StopEverything: stopEverything,
SchedulingQueue: podQueue,
Profiles: profiles,
logger: logger,
}
sched.NextPod = podQueue.Pop
sched.applyDefaultHandlers()
if err = addAllEventHandlers(sched, informerFactory, dynInformerFactory, unionedGVKs(queueingHintsPerProfile)); err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("adding event handlers: %w", err)
}
return sched, nil
}
podQueue 数据结构如下:
type PriorityQueue struct {
*nominator
stop chan struct{}
clock clock.Clock
// pod initial backoff duration.
podInitialBackoffDuration time.Duration
// pod maximum backoff duration.
podMaxBackoffDuration time.Duration
// the maximum time a pod can stay in the unschedulablePods.
podMaxInUnschedulablePodsDuration time.Duration
cond sync.Cond
// inFlightPods holds the UID of all pods which have been popped out for which Done
// hasn't been called yet - in other words, all pods that are currently being
// processed (being scheduled, in permit, or in the binding cycle).
//
// The values in the map are the entry of each pod in the inFlightEvents list.
// The value of that entry is the *v1.Pod at the time that scheduling of that
// pod started, which can be useful for logging or debugging.
inFlightPods map[types.UID]*list.Element
// inFlightEvents holds the events received by the scheduling queue
// (entry value is clusterEvent) together with in-flight pods (entry
// value is *v1.Pod). Entries get added at the end while the mutex is
// locked, so they get serialized.
//
// The pod entries are added in Pop and used to track which events
// occurred after the pod scheduling attempt for that pod started.
// They get removed when the scheduling attempt is done, at which
// point all events that occurred in the meantime are processed.
//
// After removal of a pod, events at the start of the list are no
// longer needed because all of the other in-flight pods started
// later. Those events can be removed.
inFlightEvents *list.List
// activeQ is heap structure that scheduler actively looks at to find pods to
// schedule. Head of heap is the highest priority pod.
activeQ *heap.Heap
// podBackoffQ is a heap ordered by backoff expiry. Pods which have completed backoff
// are popped from this heap before the scheduler looks at activeQ
podBackoffQ *heap.Heap
// unschedulablePods holds pods that have been tried and determined unschedulable.
unschedulablePods *UnschedulablePods
// schedulingCycle represents sequence number of scheduling cycle and is incremented
// when a pod is popped.
schedulingCycle int64
// moveRequestCycle caches the sequence number of scheduling cycle when we
// received a move request. Unschedulable pods in and before this scheduling
// cycle will be put back to activeQueue if we were trying to schedule them
// when we received move request.
// TODO: this will be removed after SchedulingQueueHint goes to stable and the feature gate is removed.
moveRequestCycle int64
// preEnqueuePluginMap is keyed with profile name, valued with registered preEnqueue plugins.
preEnqueuePluginMap map[string][]framework.PreEnqueuePlugin
// queueingHintMap is keyed with profile name, valued with registered queueing hint functions.
queueingHintMap QueueingHintMapPerProfile
// closed indicates that the queue is closed.
// It is mainly used to let Pop() exit its control loop while waiting for an item.
closed bool
nsLister listersv1.NamespaceLister
metricsRecorder metrics.MetricAsyncRecorder
// pluginMetricsSamplePercent is the percentage of plugin metrics to be sampled.
pluginMetricsSamplePercent int
// isSchedulingQueueHintEnabled indicates whether the feature gate for the scheduling queue is enabled.
isSchedulingQueueHintEnabled bool
}
PriorityQueue 优先级队列中,包含了 activeQ、backoffQ、unschedulableQ 3 个重要的子队列:
-
activeQ:Scheduler 启动的时候所有等待被调度的 Pod 都会进入 activeQ,activeQ 会按照 Pod 的 priority 进行排序,Scheduler Pipeline 会从 activeQ 获取一个 Pod 并执行调度流程(Pipeline),当调度失败之后会直接根据情况选择进入 unschedulableQ 或者 backoffQ,如果在当前 Pod 调度期间 Node Cache、Pod Cache 等 Scheduler Cache 有变化就进入 backoffQ,否则进入 unschedulableQ。
-
podBackoffQ(backoffQ)称为 退避队列,持有从 unschedulablePods 中移走的 Pod,并将在其 backoff periods 退避期结束时移动到 activeQ 队列。Pod 在退避队列中等待并定期尝试进行重新调度。重新调度的频率会按照一个指数级的算法定时增加,从而充分探索可用的资源,直到找到可以分配给该 Pod 的节点。
-
unschedulablePods(unschedulableQ):不可调度 Pod 的列表,也可以将其理解为不可调度队列 unschedulable queue,持有已尝试进行调度且当前确定为不可调度的 Pod。
unschedulableQ 会定期较长时间(例如 60 秒)刷入 activeQ 或者 backoffQ,或者在 Scheduler Cache 发生变化的时候触发关联的 Pod 刷入 activeQ 或者 backoffQ。
backoffQ 采用 backoff 机制,会让待调度的 Pod 比 unschedulableQ 更快地进入 activeQ 进行重新调度。
提示:Node Cache、Pod Cache 有变化,就意味着调度失败的 Pod 可能会在新的调度上下文中被调度成功,所以需要放在 activeQ 中。
Pod 在 3 个队列的移动过程如下图所示:
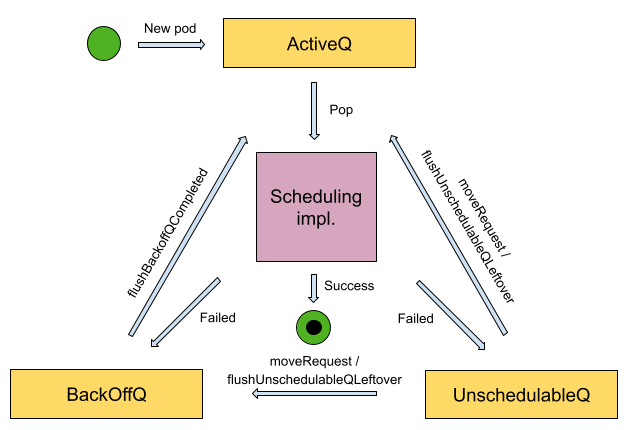
这3个队列都是 Kubernetes 调度器的基本导向队列,调度器将使用其内置策略和其他算法来对它们进行维护和管理。
在创建调度队列时,对队列进行了以下设置:
-
指定了队列中 Pod 排序方法,默认为调度策略列表中第一个调度策略的 QueueSortFunc 函数。
-
PodInitialBackoffDuration 定义了在尝试调度失败后的初始回退时间间隔。当调度器无法成功调度 Pod 时,会等待一段时间后再尝试重新调度。这个参数指定了初始的等待时间间隔。
-
PodMaxBackoffDuration 定义了在尝试调度失败后的最大回退时间间隔。如果调度器多次尝试调度失败,会逐渐增加等待时间间隔,但不会超过此参数定义的最大值。
-
PodMaxInUnschedulablePodsDuration 定义了 Pod 在无法调度的情况下最大的等待时间。如果 Pod 一直无法被调度成功,会在达到此参数定义的最大等待时间后被放弃。
-
PreEnqueuePluginMap 是一个映射,将调度器的预调度插件与其配置进行关联。预调度插件在调度器尝试将 Pod 放入调度队列之前运行,用于对 Pod 进行预处理或过滤。
-
QueueingHintMapPerProfile 是一个映射,将调度器的队列提示(queueing hint)与调度器配置文件中的配置文件进行关联。队列提示是指在调度器中为 Pod 提供的提示,以影响其在调度队列中的位置和优先级。
-
PluginMetricsSamplePercent 定义了插件度量指标采样的百分比。在 Kubernetes 调度器中,插件可以生成度量指标来监控其性能和效果。此参数定义了对多少调度周期进行度量指标采样。
上面,我们创建了优先级调度队列,那么 Pod 具体如何入队和出队呢?入队和出队,是 Pod 调度中非常关键的流程。
-
入队:新增一个待调度的 Pod。
-
出队:去除一个待调度的 Pod 进行调度。
接下来,我们就来看下 kube-scheduler 中 Pod 具体是如何入队和出队的。
Pod 入队列
kube-scheduler 中通过 Kubernetes EventHandler 的方式,在 Pod、Node 有变更时将 Pod 添加到指定的调度队列和缓冲中。如果 len(pod.Spec.NodeName) == 0,说明 Pod 还没有被调度过,则会将 Pod 添加到 activeQ 或 podBackoffQ。
Pod 出队列(准备调度)
在 cmd/kube-scheduler/app/server.go 文件中,通过 sched.Run 启动了调度器。sched.Run 函数实现如下:
func (sched *Scheduler) Run(ctx context.Context) {
logger := klog.FromContext(ctx)
sched.SchedulingQueue.Run(logger)
// We need to start scheduleOne loop in a dedicated goroutine,
// because scheduleOne function hangs on getting the next item
// from the SchedulingQueue.
// If there are no new pods to schedule, it will be hanging there
// and if done in this goroutine it will be blocking closing
// SchedulingQueue, in effect causing a deadlock on shutdown.
go wait.UntilWithContext(ctx, sched.scheduleOne, 0)
<-ctx.Done()
sched.SchedulingQueue.Close()
}
首先,通过调用 sched.SchedulingQueue.Run() 启用优先队列服务。
// Run starts the goroutine to pump from podBackoffQ to activeQ
func (p *PriorityQueue) Run(logger klog.Logger) {
go wait.Until(func() {
p.flushBackoffQCompleted(logger)
}, 1.0*time.Second, p.stop)
go wait.Until(func() {
p.flushUnschedulablePodsLeftover(logger)
}, 30*time.Second, p.stop)
}
这里就干两件事:
-
每 1 秒执行一个 p.flushBackoffQCompleted() 函数,将所有已完成的 Pod 从 backoffQ 队列移动到 activeQ 队列。
-
每 30 秒执行一次 flushUnschedulablePodsLeftover() 函数,将所有停留在 unschedulablePods 中时间超出 podMaxInUnschedulablePodsDuration 的 Pod 移动到 backoffQ 或 activeQ 队列。
接着,go wait.UntilWithContext(ctx, sched.scheduleOne, 0) 会新建一个 goroutine,在 goroutine 中,会不断地循环执行 sched.scheduleOne。sched.scheduleOne 用来从 Pod 调度队列中取出一个待调度的 Pod,根据调度策略和插件进行 Pod 调度。
调度 Pod 流程(调度始点:scheduleOne 函数)
调度流程是 kube-scheduler 最核心的流程。为了能够让你充分理解其调度逻辑,解析每个核心调度方法具体实现时,我可能会讲得稍微细一点。
scheduleOne 函数实现了对一个 Pod 的完整调度逻辑,实现代码如下:
// scheduleOne does the entire scheduling workflow for a single pod. It is serialized on the scheduling algorithm's host fitting.
func (sched *Scheduler) scheduleOne(ctx context.Context) {
logger := klog.FromContext(ctx)
// 从 scheduler 的待调度 pod 队列中取出一个 pod 进行调度
podInfo, err := sched.NextPod(logger)
if err != nil {
logger.Error(err, "Error while retrieving next pod from scheduling queue")
return
}
// 如果获取的 podInfo 或p odInfo.Pod 为 nil,说明队列中暂无需要调度的 Pod,直接退出当前调度循环
if podInfo == nil || podInfo.Pod == nil {
return
}
pod := podInfo.Pod
// TODO(knelasevero): Remove duplicated keys from log entry calls
// When contextualized logging hits GA
// https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes/issues/111672
logger = klog.LoggerWithValues(logger, "pod", klog.KObj(pod))
ctx = klog.NewContext(ctx, logger)
logger.V(4).Info("About to try and schedule pod", "pod", klog.KObj(pod))
// sched.frameworkForPod(pod) 函数调用,会根据 pod.Spec.SchedulerName 获取 pod 指定的调度策略的名字。
// 之后,从调度策略注册表中,获取个该调度策略的 framework.Framework,framework.Framework包含了调度需要的调度插件。
fwk, err := sched.frameworkForPod(pod)
if err != nil {
// This shouldn't happen, because we only accept for scheduling the pods
// which specify a scheduler name that matches one of the profiles.
logger.Error(err, "Error occurred")
return
}
// 检查是否需要调度,以下 Pod 不会被调度:
// 1. 如果 Pod 正在被删除中,则不会调度该 Pod;
// 2. 如果该 Pod 已经被 Assumed 过,则不会调度该 Pod。被 Assumed 过的 Pod 会被存放到一个叫 assumedPods 的缓存中。
if sched.skipPodSchedule(ctx, fwk, pod) {
return
}
logger.V(3).Info("Attempting to schedule pod", "pod", klog.KObj(pod))
// Synchronously attempt to find a fit for the pod.
start := time.Now()
// 如果 Pod 能够被调度,会使用 framework.NewCycleState() 函数,创建一个新的调度周期状态对象state,
// 用来保存调度过程中的状态信息,比如已经被调度的 Pod、还未被调度的 Pod 等。
// 这个调度周期状态对象在 kube-scheduler 的调度过程中会被使用,来记录和管理调度的状态,具体通常会包含以下信息:
// 1. 已经被调度的 Pod 列表:记录已经被成功调度到节点上的 Pod。
// 2. 待调度的 Pod 列表:记录还未被调度的 Pod。
// 3. 节点状态信息:记录集群中各个节点的状态,比如资源利用情况、标签信息等。
// 4. 调度器的配置信息:记录调度器的配置参数,比如调度策略、优先级规则等。
// 这些信息会在 kube-scheduler 的调度循环中被不断更新和引用,以保证调度器能够根据最新的状态信息为新的 Pod 进行合适的节点选择。
state := framework.NewCycleState()
state.SetRecordPluginMetrics(rand.Intn(100) < pluginMetricsSamplePercent)
// Initialize an empty podsToActivate struct, which will be filled up by plugins or stay empty.
podsToActivate := framework.NewPodsToActivate()
state.Write(framework.PodsToActivateKey, podsToActivate)
schedulingCycleCtx, cancel := context.WithCancel(ctx)
defer cancel()
// 调用 sched.schedulingCycle 函数,进入到调度循环中,调度循环的输出是调度结果。
scheduleResult, assumedPodInfo, status := sched.schedulingCycle(schedulingCycleCtx, state, fwk, podInfo, start, podsToActivate)
if !status.IsSuccess() {
sched.FailureHandler(schedulingCycleCtx, fwk, assumedPodInfo, status, scheduleResult.nominatingInfo, start)
return
}
// bind the pod to its host asynchronously (we can do this b/c of the assumption step above).
// 如果调度成功,则会创建一个 goroutine,该 goroutine 是一个绑定循环,用来异步的将待调度的 Pod 和分配的 Node 进行绑定,
// 也即设置 pod.Spec.NodeName 字段。可以看到,调度 Pod 是同步的,但是绑定 Pod 的调度结果时,是异步的,以提高调度并发。
go func() {
bindingCycleCtx, cancel := context.WithCancel(ctx)
defer cancel()
metrics.Goroutines.WithLabelValues(metrics.Binding).Inc()
defer metrics.Goroutines.WithLabelValues(metrics.Binding).Dec()
// 进度到绑定循环中,绑定循环后面会详细介绍
status := sched.bindingCycle(bindingCycleCtx, state, fwk, scheduleResult, assumedPodInfo, start, podsToActivate)
if !status.IsSuccess() {
sched.handleBindingCycleError(bindingCycleCtx, state, fwk, assumedPodInfo, start, scheduleResult, status)
return
}
// Usually, DonePod is called inside the scheduling queue,
// but in this case, we need to call it here because this Pod won't go back to the scheduling queue.
// 标记 Pod 调度完成
sched.SchedulingQueue.Done(assumedPodInfo.Pod.UID)
}()
}
调度循环(Scheduling Cycle)
当获取到一个待调度的 Pod 后,就会调用 sched.schedulingCycle 进入到调度循环中。schedulingCycle 函数执行 Pod 调度逻辑。schedulingCycle 函数中,会按顺序执行以下调度扩展点:
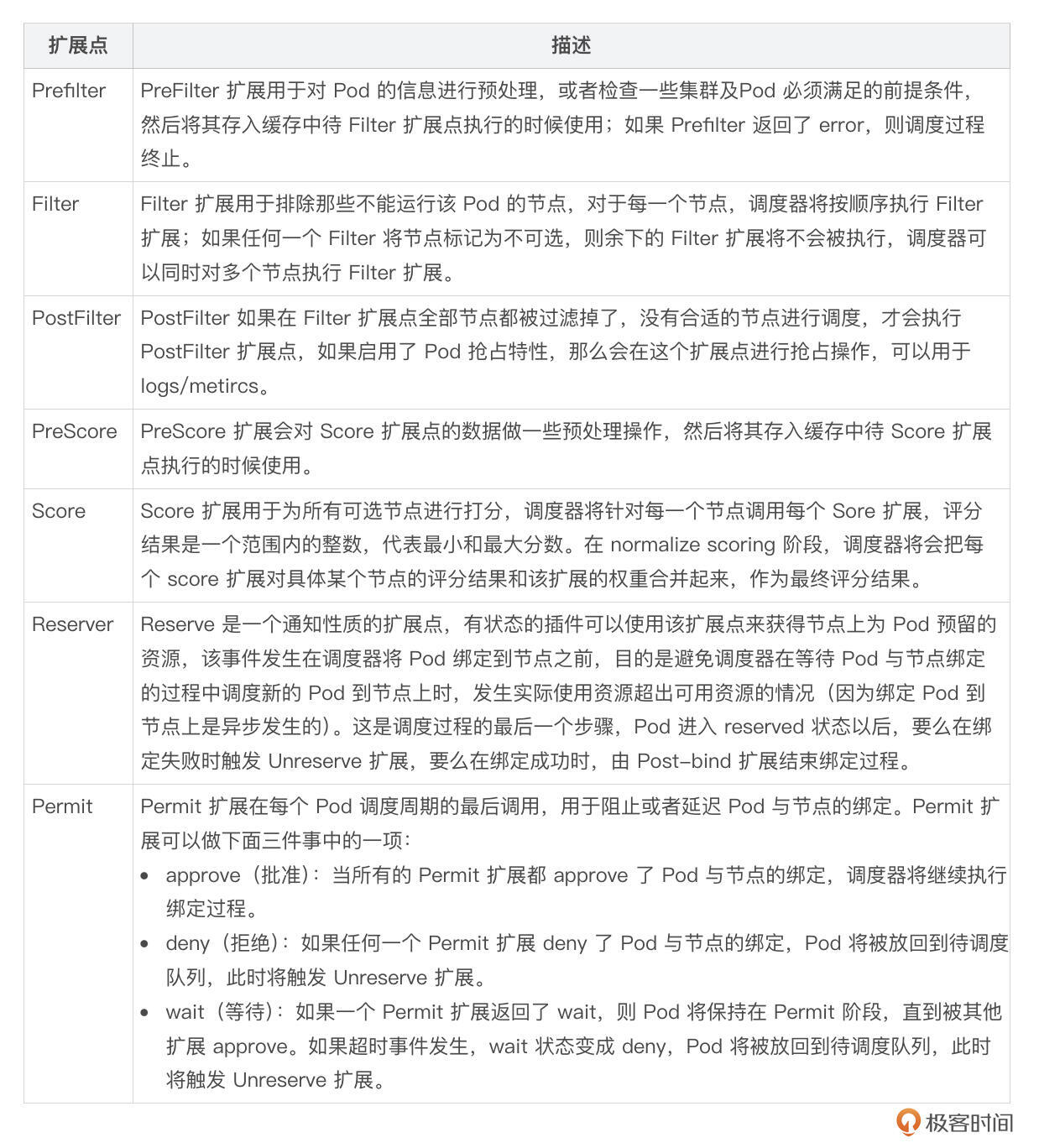
schedulingCycle 比较重要,所以这里我列出完整的代码,并在核心的代码调用处加上注释,方便你理解 schedulingCycle 函数中的核心调度逻辑:
// schedulingCycle tries to schedule a single Pod.
func (sched *Scheduler) schedulingCycle(
ctx context.Context,
state *framework.CycleState,
fwk framework.Framework,
podInfo *framework.QueuedPodInfo,
start time.Time,
podsToActivate *framework.PodsToActivate,
) (ScheduleResult, *framework.QueuedPodInfo, *framework.Status) {
logger := klog.FromContext(ctx)
// 获取调度的 Pod 对象,类型为 *v1.Pod
pod := podInfo.Pod
// 尝试调度该 Pod 到合适的 Node 上,Node 列表通过 sched.nodeInfoSnapshot.NodeInfos().List() 方法来获取
scheduleResult, err := sched.SchedulePod(ctx, fwk, state, pod)
if err != nil {
// 如果返回的调度错误是 ErrNoNodesAvailable,则调度失败,退出调度循环
if err == ErrNoNodesAvailable {
status := framework.NewStatus(framework.UnschedulableAndUnresolvable).WithError(err)
return ScheduleResult{nominatingInfo: clearNominatedNode}, podInfo, status
}
fitError, ok := err.(*framework.FitError)
if !ok {
logger.Error(err, "Error selecting node for pod", "pod", klog.KObj(pod))
return ScheduleResult{nominatingInfo: clearNominatedNode}, podInfo, framework.AsStatus(err)
}
// SchedulePod() may have failed because the pod would not fit on any host, so we try to
// preempt, with the expectation that the next time the pod is tried for scheduling it
// will fit due to the preemption. It is also possible that a different pod will schedule
// into the resources that were preempted, but this is harmless.
// 执行 PostFilter 调度扩展点
if !fwk.HasPostFilterPlugins() {
logger.V(3).Info("No PostFilter plugins are registered, so no preemption will be performed")
return ScheduleResult{}, podInfo, framework.NewStatus(framework.Unschedulable).WithError(err)
}
// Run PostFilter plugins to attempt to make the pod schedulable in a future scheduling cycle.
// 如果调度失败,并且调度策略的插件列表中,有插件实现了 PostFilter 扩展点,则执行调度抢占逻辑
result, status := fwk.RunPostFilterPlugins(ctx, state, pod, fitError.Diagnosis.NodeToStatusMap)
msg := status.Message()
fitError.Diagnosis.PostFilterMsg = msg
if status.Code() == framework.Error {
logger.Error(nil, "Status after running PostFilter plugins for pod", "pod", klog.KObj(pod), "status", msg)
} else {
logger.V(5).Info("Status after running PostFilter plugins for pod", "pod", klog.KObj(pod), "status", msg)
}
var nominatingInfo *framework.NominatingInfo
if result != nil {
nominatingInfo = result.NominatingInfo
}
return ScheduleResult{nominatingInfo: nominatingInfo}, podInfo, framework.NewStatus(framework.Unschedulable).WithError(err)
}
metrics.SchedulingAlgorithmLatency.Observe(metrics.SinceInSeconds(start))
// Tell the cache to assume that a pod now is running on a given node, even though it hasn't been bound yet.
// This allows us to keep scheduling without waiting on binding to occur.
assumedPodInfo := podInfo.DeepCopy()
assumedPod := assumedPodInfo.Pod
// assume modifies `assumedPod` by setting NodeName=scheduleResult.SuggestedHost
// 调用 sched.assume,在 scheduler 的 cache 中记录这个 pod 已经调度了,因为更新 pod 的 nodeName 是异步操作,
// 防止 pod 被重复调度
err = sched.assume(logger, assumedPod, scheduleResult.SuggestedHost)
if err != nil {
// This is most probably result of a BUG in retrying logic.
// We report an error here so that pod scheduling can be retried.
// This relies on the fact that Error will check if the pod has been bound
// to a node and if so will not add it back to the unscheduled pods queue
// (otherwise this would cause an infinite loop).
return ScheduleResult{nominatingInfo: clearNominatedNode}, assumedPodInfo, framework.AsStatus(err)
}
// Run the Reserve method of reserve plugins.
// 执行 Reserve 插件扩展点,Reserve 是一个通知性质的扩展点,有状态的插件可以使用该扩展点来获得节点上为 Pod 预留的资源,
// 该事件发生在调度器将 Pod 绑定到节点之前,目的是避免调度器在等待 Pod 与节点绑定的过程中调度新的 Pod 到节点上时,
// 发生实际使用资源超出可用资源的情况(因为绑定 Pod 到节点上是异步发生的)。这是调度过程的最后一个步骤,
// Pod 进入 reserved 状态以后,要么在绑定失败时触发 Unreserve 扩展,要么在绑定成功时,由 Post-bind 扩展结束绑定过程。
if sts := fwk.RunReservePluginsReserve(ctx, state, assumedPod, scheduleResult.SuggestedHost); !sts.IsSuccess() {
// trigger un-reserve to clean up state associated with the reserved Pod
fwk.RunReservePluginsUnreserve(ctx, state, assumedPod, scheduleResult.SuggestedHost)
if forgetErr := sched.Cache.ForgetPod(logger, assumedPod); forgetErr != nil {
logger.Error(forgetErr, "Scheduler cache ForgetPod failed")
}
if sts.IsRejected() {
fitErr := &framework.FitError{
NumAllNodes: 1,
Pod: pod,
Diagnosis: framework.Diagnosis{
NodeToStatusMap: framework.NodeToStatusMap{scheduleResult.SuggestedHost: sts},
},
}
fitErr.Diagnosis.AddPluginStatus(sts)
return ScheduleResult{nominatingInfo: clearNominatedNode}, assumedPodInfo, framework.NewStatus(sts.Code()).WithError(fitErr)
}
return ScheduleResult{nominatingInfo: clearNominatedNode}, assumedPodInfo, sts
}
// Run "permit" plugins.
// 执行 Permit 插件扩展点,用于阻止或者延迟 Pod 与节点的绑定。Permit 扩展可以做下面三件事中的一项:
// 1. approve(批准):当所有的 permit 扩展都 approve 了 Pod 与节点的绑定,调度器将继续执行绑定过程;
// 2. deny(拒绝):如果任何一个 permit 扩展 deny 了 Pod 与节点的绑定,Pod 将被放回到待调度队列,此时将触发 Unreserve 扩展;
// 3. wait(等待):如果一个 permit 扩展返回了 wait,则 Pod 将保持在 permit 阶段,直到被其他扩展 approve。
// 如果超时事件发生,wait 状态变成 deny,Pod 将被放回到待调度队列,此时将触发 Unreserve 扩展
// 为某些资源预留(reserve)空间,以确保在节点上可以为指定的 Pod 预留需要的资源。
runPermitStatus := fwk.RunPermitPlugins(ctx, state, assumedPod, scheduleResult.SuggestedHost)
if !runPermitStatus.IsWait() && !runPermitStatus.IsSuccess() {
// trigger un-reserve to clean up state associated with the reserved Pod
fwk.RunReservePluginsUnreserve(ctx, state, assumedPod, scheduleResult.SuggestedHost)
if forgetErr := sched.Cache.ForgetPod(logger, assumedPod); forgetErr != nil {
logger.Error(forgetErr, "Scheduler cache ForgetPod failed")
}
if runPermitStatus.IsRejected() {
fitErr := &framework.FitError{
NumAllNodes: 1,
Pod: pod,
Diagnosis: framework.Diagnosis{
NodeToStatusMap: framework.NodeToStatusMap{scheduleResult.SuggestedHost: runPermitStatus},
},
}
fitErr.Diagnosis.AddPluginStatus(runPermitStatus)
return ScheduleResult{nominatingInfo: clearNominatedNode}, assumedPodInfo, framework.NewStatus(runPermitStatus.Code()).WithError(fitErr)
}
return ScheduleResult{nominatingInfo: clearNominatedNode}, assumedPodInfo, runPermitStatus
}
// At the end of a successful scheduling cycle, pop and move up Pods if needed.
if len(podsToActivate.Map) != 0 {
sched.SchedulingQueue.Activate(logger, podsToActivate.Map)
// Clear the entries after activation.
podsToActivate.Map = make(map[string]*v1.Pod)
}
return scheduleResult, assumedPodInfo, nil
}
schedulingCycle 函数会调用 sched.SchedulePod 进行 Pod 调度,sched.SchedulePod 的具体实现如下:
// schedulePod tries to schedule the given pod to one of the nodes in the node list.
// If it succeeds, it will return the name of the node.
// If it fails, it will return a FitError with reasons.
func (sched *Scheduler) schedulePod(ctx context.Context, fwk framework.Framework, state *framework.CycleState, pod *v1.Pod) (resultScheduleResult, err error) {
trace := utiltrace.New("Scheduling", utiltrace.Field{Key: "namespace", Value: pod.Namespace}, utiltrace.Field{Key: "name", Value: pod.Name})
defer trace.LogIfLong(100 * time.Millisecond)
// 更新调度器的缓存快照,以确保调度器的节点信息是最新的
if err := sched.Cache.UpdateSnapshot(klog.FromContext(ctx), sched.nodeInfoSnapshot); err != nil {
return result, err
}
trace.Step("Snapshotting scheduler cache and node infos done")
// 如果缓存快照中,没有可调度的 Node,则直接返回 ErrNoNodesAvailable 错误
if sched.nodeInfoSnapshot.NumNodes() == 0 {
return result, ErrNoNodesAvailable
}
// 调用 sched.findNodesThatFitPod 方法,查找适合调度给定 Pod 的节点,获取可行节点列表、诊断信息和可能的错误
feasibleNodes, diagnosis, err := sched.findNodesThatFitPod(ctx, fwk, state, pod)
if err != nil {
return result, err
}
trace.Step("Computing predicates done")
// 如果没有找到适合的节点,返回一个 FitError,其中包含未能调度的 Pod、所有节点数量和诊断信息
if len(feasibleNodes) == 0 {
return result, &framework.FitError{
Pod: pod,
NumAllNodes: sched.nodeInfoSnapshot.NumNodes(),
Diagnosis: diagnosis,
}
}
// When only one node after predicate, just use it.
// 如果只有一个适合的节点,则直接将 Pod 调度到该节点上
if len(feasibleNodes) == 1 {
return ScheduleResult{
SuggestedHost: feasibleNodes[0].Name,
EvaluatedNodes: 1 + len(diagnosis.NodeToStatusMap),
FeasibleNodes: 1,
}, nil
}
// 调用 prioritizeNodes 方法对可行节点进行优先级排序,获取一个优先级列表
// prioritizeNodes 函数中执行了 PreScore、Score 扩展点
priorityList, err := prioritizeNodes(ctx, sched.Extenders, fwk, state, pod, feasibleNodes)
if err != nil {
return result, err
}
// 调用 selectHost 方法选择最终的节点,并返回建议的节点名称、评估节点的数量和可行节点的数量
host, _, err := selectHost(priorityList, numberOfHighestScoredNodesToReport)
trace.Step("Prioritizing done")
return ScheduleResult{
SuggestedHost: host,
EvaluatedNodes: len(feasibleNodes) + len(diagnosis.NodeToStatusMap),
FeasibleNodes: len(feasibleNodes),
}, err
}
schedulePod 根据一系列的调度扩展点,最终为 Pod 选择一个最佳调度节点。schedulePod 方法中有 3 个核心函数调用:
-
sched.findNodesThatFitPod(ctx, fwk, state, pod):查找适合调度给定 Pod 的节点,获取可行节点列表、诊断信息和可能的错误。
-
prioritizeNodes(ctx, sched.Extenders, fwk, state, pod, feasibleNodes):对可行节点进行优先级排序,获取一个优先级列表。
-
selectHost(priorityList, numberOfHighestScoredNodesToReport):选择最终的节点,并返回建议的节点名称、评估节点的数量和可行节点的数量。
接下来,我们分别来看下 findNodesThatFitPod、prioritizeNodes、selectHost 函数的具体实现。
findNodesThatFitPod 方法实现了 kube-scheduler 调度扩展点中的 PreFilter、Filter 扩展点,具体实现代码如下:
// findNodesThatFitPod 实现了 kube-scheduler 调度扩展点中的以下扩展点:PreFilter、Filter 扩展点
func (sched *Scheduler) findNodesThatFitPod(ctx context.Context, fwk framework.Framework, state *framework.CycleState, pod *v1.Pod) ([]*v1.Node,framework.Diagnosis, error) {
logger := klog.FromContext(ctx)
diagnosis := framework.Diagnosis{
NodeToStatusMap: make(framework.NodeToStatusMap),
}
// 获取待调度的节点列表
allNodes, err := sched.nodeInfoSnapshot.NodeInfos().List()
if err != nil {
return nil, diagnosis, err
}
// 执行 PreFilter 扩展点
preRes, s := fwk.RunPreFilterPlugins(ctx, state, pod)
// 如果预过滤结果不成功,根据状态处理不同情况
// 1. 如果状态不是被拒绝,则将所有节点标记为相同状态,并记录预过滤消息;
// 2. 返回相应的诊断信息和错误。
if !s.IsSuccess() {
if !s.IsRejected() {
return nil, diagnosis, s.AsError()
}
// All nodes in NodeToStatusMap will have the same status so that they can be handled in the preemption.
// Some non trivial refactoring is needed to avoid this copy.
for _, n := range allNodes {
diagnosis.NodeToStatusMap[n.Node().Name] = s
}
// Record the messages from PreFilter in Diagnosis.PreFilterMsg.
msg := s.Message()
diagnosis.PreFilterMsg = msg
logger.V(5).Info("Status after running PreFilter plugins for pod", "pod", klog.KObj(pod), "status", msg)
diagnosis.AddPluginStatus(s)
return nil, diagnosis, nil
}
// "NominatedNodeName" can potentially be set in a previous scheduling cycle as a result of preemption.
// This node is likely the only candidate that will fit the pod, and hence we try it first before iterating over all nodes.
if len(pod.Status.NominatedNodeName) > 0 {
feasibleNodes, err := sched.evaluateNominatedNode(ctx, pod, fwk, state, diagnosis)
if err != nil {
logger.Error(err, "Evaluation failed on nominated node", "pod", klog.KObj(pod), "node", pod.Status.NominatedNodeName)
}
// Nominated node passes all the filters, scheduler is good to assign this node to the pod.
if len(feasibleNodes) != 0 {
return feasibleNodes, diagnosis, nil
}
}
nodes := allNodes
if !preRes.AllNodes() {
nodes = make([]*framework.NodeInfo, 0, len(preRes.NodeNames))
for n := range preRes.NodeNames {
nInfo, err := sched.nodeInfoSnapshot.NodeInfos().Get(n)
if err != nil {
return nil, diagnosis, err
}
nodes = append(nodes, nInfo)
}
}
// 运行 Filter 扩展点,对节点进行过滤,获取符合条件的节点列表
feasibleNodes, err := sched.findNodesThatPassFilters(ctx, fwk, state, pod, &diagnosis, nodes)
// always try to update the sched.nextStartNodeIndex regardless of whether an error has occurred
// this is helpful to make sure that all the nodes have a chance to be searched
processedNodes := len(feasibleNodes) + len(diagnosis.NodeToStatusMap)
sched.nextStartNodeIndex = (sched.nextStartNodeIndex + processedNodes) % len(nodes)
if err != nil {
return nil, diagnosis, err
}
feasibleNodes, err = findNodesThatPassExtenders(ctx, sched.Extenders, pod, feasibleNodes, diagnosis.NodeToStatusMap)
if err != nil {
return nil, diagnosis, err
}
return feasibleNodes, diagnosis, nil
}
prioritizeNodes 函数代码实现如下:
// prioritizeNodes prioritizes the nodes by running the score plugins,
// which return a score for each node from the call to RunScorePlugins().
// The scores from each plugin are added together to make the score for that node, then
// any extenders are run as well.
// All scores are finally combined (added) to get the total weighted scores of all nodes
func prioritizeNodes(
ctx context.Context,
extenders []framework.Extender,
fwk framework.Framework,
state *framework.CycleState,
pod *v1.Pod,
nodes []*v1.Node,
) ([]framework.NodePluginScores, error) {
logger := klog.FromContext(ctx)
// If no priority configs are provided, then all nodes will have a score of one.
// This is required to generate the priority list in the required format
if len(extenders) == 0 && !fwk.HasScorePlugins() {
result := make([]framework.NodePluginScores, 0, len(nodes))
for i := range nodes {
result = append(result, framework.NodePluginScores{
Name: nodes[i].Name,
TotalScore: 1,
})
}
return result, nil
}
// Run PreScore plugins.
preScoreStatus := fwk.RunPreScorePlugins(ctx, state, pod, nodes)
if !preScoreStatus.IsSuccess() {
return nil, preScoreStatus.AsError()
}
// Run the Score plugins.
nodesScores, scoreStatus := fwk.RunScorePlugins(ctx, state, pod, nodes)
if !scoreStatus.IsSuccess() {
return nil, scoreStatus.AsError()
}
// Additional details logged at level 10 if enabled.
loggerVTen := logger.V(10)
if loggerVTen.Enabled() {
for _, nodeScore := range nodesScores {
for _, pluginScore := range nodeScore.Scores {
loggerVTen.Info("Plugin scored node for pod", "pod", klog.KObj(pod), "plugin", pluginScore.Name, "node", nodeScore.Name, "score", pluginScore.Score)
}
}
}
if len(extenders) != 0 && nodes != nil {
// allNodeExtendersScores has all extenders scores for all nodes.
// It is keyed with node name.
allNodeExtendersScores := make(map[string]*framework.NodePluginScores, len(nodes))
var mu sync.Mutex
var wg sync.WaitGroup
for i := range extenders {
if !extenders[i].IsInterested(pod) {
continue
}
wg.Add(1)
go func(extIndex int) {
metrics.Goroutines.WithLabelValues(metrics.PrioritizingExtender).Inc()
defer func() {
metrics.Goroutines.WithLabelValues(metrics.PrioritizingExtender).Dec()
wg.Done()
}()
prioritizedList, weight, err := extenders[extIndex].Prioritize(pod, nodes)
if err != nil {
// Prioritization errors from extender can be ignored, let k8s/other extenders determine the priorities
logger.V(5).Info("Failed to run extender's priority function. No score given by this extender.", "error", err, "pod", klog.KObj(pod), "extender", extenders[extIndex].Name())
return
}
mu.Lock()
defer mu.Unlock()
for i := range *prioritizedList {
nodename := (*prioritizedList)[i].Host
score := (*prioritizedList)[i].Score
if loggerVTen.Enabled() {
loggerVTen.Info("Extender scored node for pod", "pod", klog.KObj(pod), "extender", extenders[extIndex].Name(), "node", nodename, "score", score)
}
// MaxExtenderPriority may diverge from the max priority used in the scheduler and defined by MaxNodeScore,
// therefore we need to scale the score returned by extenders to the score range used by the scheduler.
finalscore := score * weight * (framework.MaxNodeScore / extenderv1.MaxExtenderPriority)
if allNodeExtendersScores[nodename] == nil {
allNodeExtendersScores[nodename] = &framework.NodePluginScores{
Name: nodename,
Scores: make([]framework.PluginScore, 0, len(extenders)),
}
}
allNodeExtendersScores[nodename].Scores = append(allNodeExtendersScores[nodename].Scores, framework.PluginScore{
Name: extenders[extIndex].Name(),
Score: finalscore,
})
allNodeExtendersScores[nodename].TotalScore += finalscore
}
}(i)
}
// wait for all go routines to finish
wg.Wait()
for i := range nodesScores {
if score, ok := allNodeExtendersScores[nodes[i].Name]; ok {
nodesScores[i].Scores = append(nodesScores[i].Scores, score.Scores...)
nodesScores[i].TotalScore += score.TotalScore
}
}
}
if loggerVTen.Enabled() {
for i := range nodesScores {
loggerVTen.Info("Calculated node's final score for pod", "pod", klog.KObj(pod), "node", nodesScores[i].Name, "score", nodesScores[i].TotalScore)
}
}
return nodesScores, nil
}
selectHost 函数代码如下:
// selectHost takes a prioritized list of nodes and then picks one
// in a reservoir sampling manner from the nodes that had the highest score.
// It also returns the top {count} Nodes,
// and the top of the list will be always the selected host.
func selectHost(nodeScoreList []framework.NodePluginScores, count int) (string, []framework.NodePluginScores, error) {
// 如果 nodeScoreList 为空,说明其中没有适合调度的 Node,直接返回空的列表
if len(nodeScoreList) == 0 {
return "", nil, errEmptyPriorityList
}
var h nodeScoreHeap = nodeScoreList
heap.Init(&h)
cntOfMaxScore := 1
selectedIndex := 0 // The top of the heap is the NodeScoreResult with the highest score.
sortedNodeScoreList := make([]framework.NodePluginScores, 0, count)
sortedNodeScoreList = append(sortedNodeScoreList, heap.Pop(&h).(framework.NodePluginScores))
// This for-loop will continue until all Nodes with the highest scores get checked for a reservoir sampling,
// and sortedNodeScoreList gets (count - 1) elements.
for ns := heap.Pop(&h).(framework.NodePluginScores); ; ns = heap.Pop(&h).(framework.NodePluginScores) {
if ns.TotalScore != sortedNodeScoreList[0].TotalScore && len(sortedNodeScoreList) == count {
break
}
if ns.TotalScore == sortedNodeScoreList[0].TotalScore {
cntOfMaxScore++
if rand.Intn(cntOfMaxScore) == 0 {
// Replace the candidate with probability of 1/cntOfMaxScore
selectedIndex = cntOfMaxScore - 1
}
}
sortedNodeScoreList = append(sortedNodeScoreList, ns)
if h.Len() == 0 {
break
}
}
if selectedIndex != 0 {
// replace the first one with selected one
previous := sortedNodeScoreList[0]
sortedNodeScoreList[0] = sortedNodeScoreList[selectedIndex]
sortedNodeScoreList[selectedIndex] = previous
}
if len(sortedNodeScoreList) > count {
sortedNodeScoreList = sortedNodeScoreList[:count]
}
return sortedNodeScoreList[0].Name, sortedNodeScoreList, nil
}
绑定循环(Binding Cycle)
在 scheduleOne 函数中,当调度循环(sched.schedulingCycle 函数调用)返回了一个可用的节点后,接下来就需要进入到绑定循环中。绑定循环可以将该 Node 和待调度的 Pod进行绑定。所谓的绑定,其实就是设置 Pod.Spec.NodeName 字段的值为节点的名字(通常是 IP 地址)。
这里,我们再次回顾下 scheduleOne 函数的实现,scheduleOne 函数实现了对 Pod 的整个调度流程,主要包含了调度循环和绑定循环。为了提高调度效率,绑定循环是在 goroutine 中进行绑定的。代码概览如下:
func (sched *Scheduler) scheduleOne(ctx context.Context) {
// ...
// 1. 调度循环
scheduleResult, assumedPodInfo, status := sched.schedulingCycle(schedulingCycleCtx, state, fwk, podInfo, start, podsToActivate)
if !status.IsSuccess() {
sched.FailureHandler(schedulingCycleCtx, fwk, assumedPodInfo, status, scheduleResult.nominatingInfo, start)
return
}
// ...
// bind the pod to its host asynchronously (we can do this b/c of the assumption step above).
go func() {
// ....
// 2. 绑定循环
status := sched.bindingCycle(bindingCycleCtx, state, fwk, scheduleResult, assumedPodInfo, start, podsToActivate)
if !status.IsSuccess() {
sched.handleBindingCycleError(bindingCycleCtx, state, fwk, assumedPodInfo, start, scheduleResult, status)
return
}
// Usually, DonePod is called inside the scheduling queue,
// but in this case, we need to call it here because this Pod won't go back to the scheduling queue.
sched.SchedulingQueue.Done(assumedPodInfo.Pod.UID)
}()
}
所以接下来,我们来看下 sched.bindingCycle 函数的具体实现,以此来理解 kube-scheduler 是如何将 Node 绑定给 Pod 的。sched.bindingCycle 实现了 PreBind、Bind 和 PostBind 调度扩展点。
sched.bindingCycle 函数代码如下:
// bindingCycle tries to bind an assumed Pod.
func (sched *Scheduler) bindingCycle(
ctx context.Context,
state *framework.CycleState,
fwk framework.Framework,
scheduleResult ScheduleResult,
assumedPodInfo *framework.QueuedPodInfo,
start time.Time,
podsToActivate *framework.PodsToActivate) *framework.Status {
logger := klog.FromContext(ctx)
assumedPod := assumedPodInfo.Pod
// Run "permit" plugins.
// 如果 Pod 处在等待状态,则等待 Pod 被所有的 Permit 插件 allow 或者 reject。否则,阻塞在此
if status := fwk.WaitOnPermit(ctx, assumedPod); !status.IsSuccess() {
if status.IsRejected() {
fitErr := &framework.FitError{
NumAllNodes: 1,
Pod: assumedPodInfo.Pod,
Diagnosis: framework.Diagnosis{
NodeToStatusMap: framework.NodeToStatusMap{scheduleResult.SuggestedHost: status},
UnschedulablePlugins: sets.New(status.Plugin()),
},
}
return framework.NewStatus(status.Code()).WithError(fitErr)
}
return status
}
// Run "prebind" plugins.
// 执行 PreBind 调度扩展点
if status := fwk.RunPreBindPlugins(ctx, state, assumedPod, scheduleResult.SuggestedHost); !status.IsSuccess() {
return status
}
// Run "bind" plugins.
// 执行 Bind 调度扩展点
if status := sched.bind(ctx, fwk, assumedPod, scheduleResult.SuggestedHost, state); !status.IsSuccess() {
return status
}
// Calculating nodeResourceString can be heavy. Avoid it if klog verbosity is below 2.
logger.V(2).Info("Successfully bound pod to node", "pod", klog.KObj(assumedPod), "node", scheduleResult.SuggestedHost, "evaluatedNodes", scheduleResult.EvaluatedNodes, "feasibleNodes", scheduleResult.FeasibleNodes)
metrics.PodScheduled(fwk.ProfileName(), metrics.SinceInSeconds(start))
metrics.PodSchedulingAttempts.Observe(float64(assumedPodInfo.Attempts))
if assumedPodInfo.InitialAttemptTimestamp != nil {
metrics.PodSchedulingDuration.WithLabelValues(getAttemptsLabel(assumedPodInfo)).Observe(metrics.SinceInSeconds(*assumedPodInfo. InitialAttemptTimestamp))
metrics.PodSchedulingSLIDuration.WithLabelValues(getAttemptsLabel(assumedPodInfo)).Observe(metrics.SinceInSeconds(*assumedPodInfo. InitialAttemptTimestamp))
}
// Run "postbind" plugins.
// 执行 PostBind 调度扩展点
fwk.RunPostBindPlugins(ctx, state, assumedPod, scheduleResult.SuggestedHost)
// At the end of a successful binding cycle, move up Pods if needed.
if len(podsToActivate.Map) != 0 {
sched.SchedulingQueue.Activate(logger, podsToActivate.Map)
// Unlike the logic in schedulingCycle(), we don't bother deleting the entries
// as `podsToActivate.Map` is no longer consumed.
}
return nil
}
课程总结
kube-scheduler 的调度原理就讲到这里,我们再整体梳理一下。
kube-scheduler 的核心调度流程从 sched.Run() 展开:首先通过 SchedulingQueue.Run() 启动三段式优先级队列(activeQ、backoffQ、unschedulableQ),随后在独立的 goroutine 中不断调用 scheduleOne 消费待调度 Pod。
在调度器实例创建阶段,系统会读取 KubeSchedulerConfiguration,加载 in-tree 与 out-of-tree 插件,构建 Extender,生成每个 Profile 对应的 framework.Framework,并据此确定队列的排序函数等运行参数。
Scheduling Framework 将一次调度分为串行执行的“调度周期”和并发执行的“绑定周期”。调度周期依次经过 PreFilter、Filter、PostFilter、PreScore、Score、Reserve、Permit 等扩展点:先筛掉不合规节点,再为可行节点打分排序,并在 Reserve 阶段做资源预留;若所有插件都批准,进入绑定周期。
绑定周期在 goroutine 中异步完成 PreBind、Bind、PostBind,实现最终的 Pod.Spec.NodeName 写入。整个架构既保持默认调度逻辑的高效,又允许开发者通过插件或 Extender 对关键节点进行定制,从而满足企业多样化的调度需求。
课后练习
-
说明 activeQ、backoffQ、unschedulableQ 三个子队列的作用差异,并举例说明 Pod 在它们之间的流转条件。
-
写出 Scheduling Framework 调度周期中 Filter 和 Score 两个扩展点的主要职责,并各列举一种可能的自定义插件场景。
-
为什么绑定周期可以与调度周期并发执行?试描述并发绑定对调度吞吐量的影响。
欢迎你在留言区与我交流讨论,如果今天的内容让你有所收获,也欢迎转发给有需要的朋友,我们下节课再见!
精选留言
2025-08-01 19:24:02