你好,我是月影。
上一节课,我们实现了一个基于简单的向量数据库的检索器(Retriever),这是实现 RAG 的第一步。
接下来我们将通过实战,把文档内容通过 SimpleRAG 写入到向量数据库,然后通过大模型进行对话。这正是一个标准的构建和使用 RAG 的过程,我们用如下的流程图来表示。
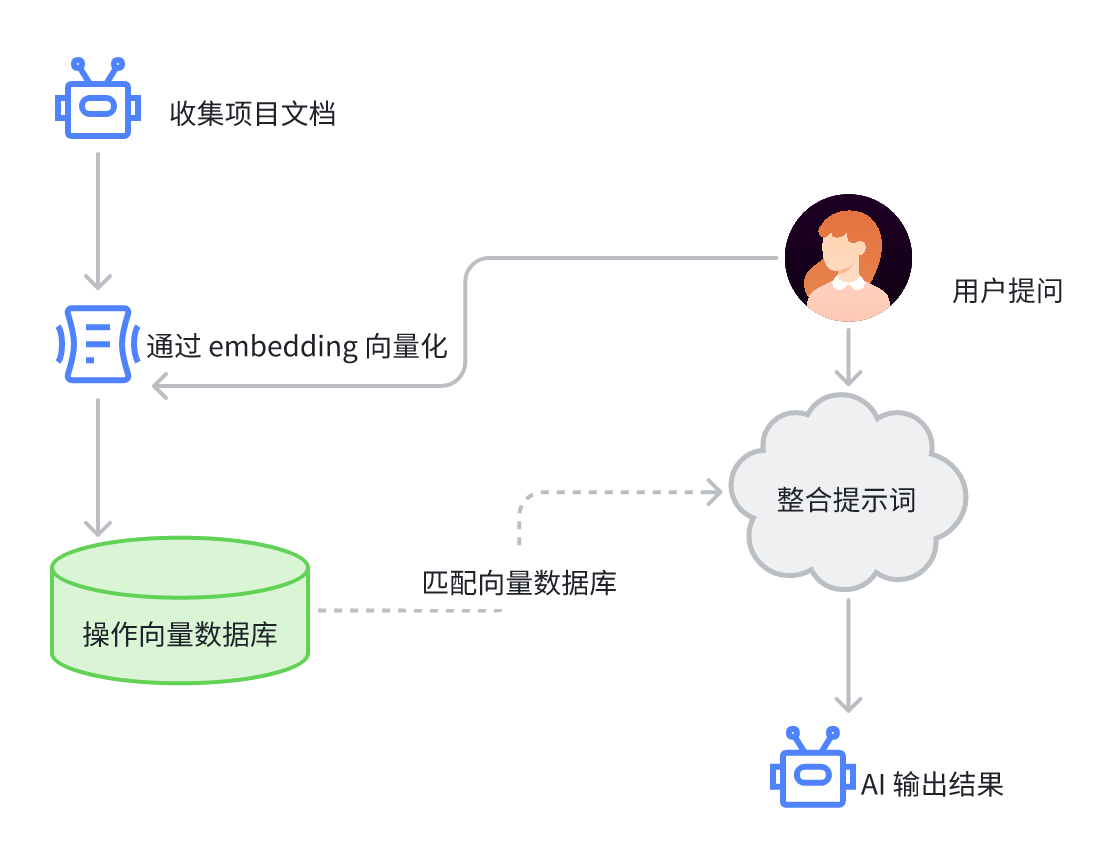
实现项目数据的向量化
在过去,传统的技术里面,要把一个项目的文档提取出来进行向量化,本身也不是很困难,无非就是根据规则遍历文件夹,找到文件夹中的特定格式文件,比如markdown文档,然后将文档中的文本内容写入到向量数据库。
这么做肯定是可以的,但这么做不够灵活。
首先它必须按照规则存放文档,AI 也没法判断文档的重要性。其次,如果项目代码更新了,文档没有及时整理,那么 AI 也无法获得最新的内容。第三,现在的 VibeCoding 工具本身分析文件目录的能力比较强,完全可以将整个项目的关键内容提取出来,可能甚至不需要文档。
所以我们可以首先实现这样的一个功能——通过 Trae 或 Cursor 的 AI 智能体,将任意开发项目的数据向量化,存储到 vectra 向量数据库中。
通过 MCP Server 来构建向量数据
要实现这个功能,我们可以构建一个 MCP Server:
#!/usr/bin/env node
/*
* MCP Server
*/
import { McpServer } from '@modelcontextprotocol/sdk/server/mcp.js';
import { StdioServerTransport } from '@modelcontextprotocol/sdk/server/stdio.js';
import { z } from 'zod';
import { loadPrompt } from './utils';
import { SimpleRag } from '../index';
import fs from 'fs/promises';
import path from 'path';
// Create an MCP server
const server = new McpServer({
name: 'AskYourLib',
version: '1.0.0',
});
// Global SimpleRag instance
let simpleRagInstance: SimpleRag | null = null;
server.tool(
'ask-your-lib-initialize',
`Initialize the vector database operations and clean up any existing .vectra directory.`,
{
},
async () => {
try {
// Check if .vectra directory exists in project root and remove it
const projectRoot = path.resolve(__dirname, '../../');
const vectraPath = path.join(projectRoot, '.vectra');
const generateMcpPrompt = await loadPrompt('generate');
try {
await fs.access(vectraPath);
await fs.rm(vectraPath, { recursive: true, force: true });
console.log('Removed existing .vectra directory');
} catch (error) {
// Directory doesn't exist, which is fine
console.log('.vectra directory does not exist, skipping removal');
}
// Create new SimpleRag instance
simpleRagInstance = new SimpleRag();
return {
content: [{
type: 'text',
text: `⚠️ The guide to follow: \n${generateMcpPrompt}\n\n`
}],
};
} catch (error) {
console.error(`Error initializing SimpleRag: ${error}`);
return {
content: [{
type: 'text',
text: `Error initializing SimpleRag: ${error}`
}],
};
}
}
)
server.tool(
'ask-your-lib-insert',
`Insert and vectorize text content into the vector database.`,
{
text: z.string(),
},
async ({ text }) => {
try {
if (!simpleRagInstance) {
return {
content: [{
type: 'text',
text: 'Database instance is not initialized. Please call ask-your-lib-initialize first.'
}],
};
}
if (!simpleRagInstance.avaliable) {
await simpleRagInstance.initialize();
}
const result = await simpleRagInstance.add(text);
return {
content: [{
type: 'text',
text: `Text inserted successfully. Inserted items: ${JSON.stringify(result)}`
}],
};
} catch (error) {
console.error(`Error inserting text: ${error}`);
return {
content: [{
type: 'text',
text: `Error inserting text: ${error}`
}],
};
}
}
)
async function main() {
// Start receiving messages on stdin and sending messages on stdout
const transport = new StdioServerTransport();
await server.connect(transport);
console.log('Server started');
}
main();
这里面的内容稍微有点复杂,但没关系,我来给你解释一下你就理解了。
首先我们给 MCP Server 创建一个叫做 ask-your-lib-initialize 的工具,它的作用是初始化 SimpleRag 实例,然后返回一段提示词,用于指导后续大模型的操作。
为了方便维护和修改,我们将这段提示词写入 src/mcp/prompts/generate.md 文件里:
generate.md
# 🧠 Vectorizing a Node.js Project and Storing in Vectra
Follow the steps below to extract valuable content from your current Node.js project, vectorize it, and store it into the Vectra vector database for AI-powered search and Q&A.
## 🔧 Step 1: Initialize the Vector Index
Run the following command in your project root directory to initialize the vector index using the MCP tool:
``bash
ask-your-lib-initialize
``
---
This will create the vector index structure to support future insertions.
## 📄 Step 2: Extract Core Project Content
Traverse the entire project and extract the following key content for vectorization:
### ✅ Project Overview
- Project background and objectives
- Installation, configuration, and usage instructions
- Key features and functionality
- Technology stack and dependency list
- Author, contributors, and community support info
(Recommended to extract from `README.md`, `docs/`, `CHANGELOG.md`, etc.)
### ✅ Source Code Insights (`.js` / `.ts` files)
- Functional descriptions and structural logic of each module
- Core functions, classes, interfaces with comments
- Meaningful inline comments or JSDoc annotations
Ensure the extracted content retains **contextual completeness** for semantic use.
### ✅ Additional Documentation (Markdown, config files, etc.)
- Development guides, API documentation, FAQs
- Descriptive fields from `package.json` (e.g., `description`, `scripts`, `dependencies`)
> 💡 **Tip**: Use glob patterns to collect `.ts`, `.js`, `.md`, `.json` files and apply smart filtering.
Organize the results into an array of strings, with each segment treated as a single vector unit.
---
## 🧬 Step 3: Vectorize and Insert into Database
Use the following command to vectorize and insert each extracted text segment:
``bash
ask-your-lib-insert --text "xxx"
``
Make sure that:
- Each segment is successfully vectorized
- Add metadata like filenames or module names if possible
- Inserted data is ordered to preserve semantic continuity
---
## ⚠️ Notes
- Avoid vectorizing trivial, empty, or duplicate content
- For long documents, consider chunking the text
- Maintain the original structure and semantics for better retrieval
---
上面这个提示词描述了 AI 接下来该怎么具体操作,为项目生成适合的向量数据。
TypeScript 不能直接 import Markdown 文本,为了加载这个提示词到代码里,我们需要一个工具函数 loadPrompt 来从 prompts 目录下读取对应的 .md 文件,我们在 src/mcp/utils.ts 里创建这个函数。
utils.ts
/**
* Load prompt content from markdown files
* @param promptName - The name of the prompt file (without extension)
* @returns Promise<string> - The content of the prompt file
*/
export async function loadPrompt(promptName: string): Promise<string> {
try {
// Get the current file's directory
const currentDir = getCurrentDir();
// Construct the path to the prompt file
const promptPath = join(currentDir, 'prompts', `${promptName}.md`);
// Read and return the file content
const content = await fs.readFile(promptPath, 'utf-8');
return content;
} catch (error) {
throw new Error(`Failed to load prompt '${promptName}': ${error instanceof Error ? error.message : 'Unknown error'}`);
}
}
还有一个细节,当我们构建项目的时候,我们需要把 prompts 下的 .md 文件也拷贝到 dist 目录下,所以我们需要在 package.json 文件里修改 build 脚本如下:
"scripts": {
"build": "tsc && mkdir -p dist/llm/prompts && cp src/llm/prompts/*.md dist/llm/prompts/",
...
这样我们就可以读取 generate.md 的内容,并通过 ask-your-lib-initialize 这个工具返回给 AI Coding 的大模型了。
ask-your-lib-initialize 除了负责调用 SimpleRAG 对象的 initial 方法来初始化实例之外,还负责将旧的数据库删除,因为我们现在还没有提供增量追加的功能,所以我们让 AI 每次生成数据时将旧数据删掉,重新生成新的数据。
接着我们创建另一个工具,叫做 ask-your-lib-insert,我们通过这个工具将内容写入向量数据库 vectra 中。
方法就是我们上一节课学过的 await simpleRagInstance.add(text) ,这个大家应该不会陌生。
这样我们可以试着使用这个 MCP Server 了。
它的配置项如下:
{
"mcpServers": {
"AskYourLib": {
"command": "npx",
"args": [
"tsx",
"/your/path/to/frontend-dev-large-model-era/rag_demo/src/mcp/server.ts"
]
}
}
}
注意将 /your/path/to/ 替换成你自己真实的文件系统目录
把这个 MCP 添加到 Trae 的配置中,别忘了给你当前使用的智能体添加这个 MCP 工具,然后就可以直接和它对话,生成向量数据了。
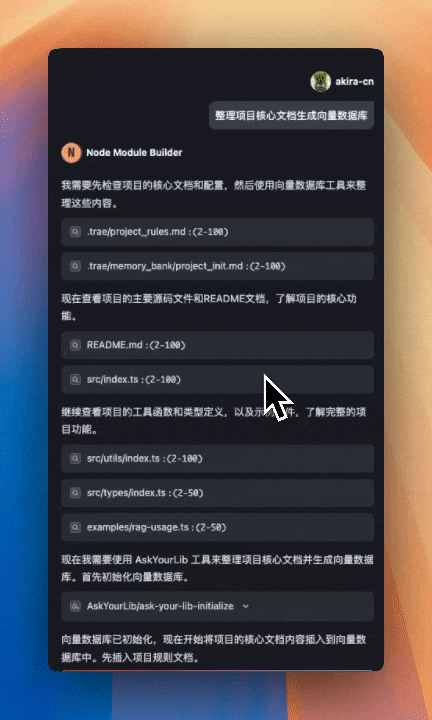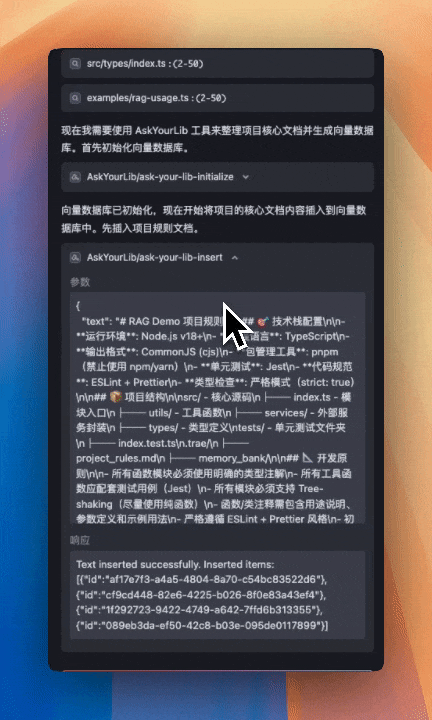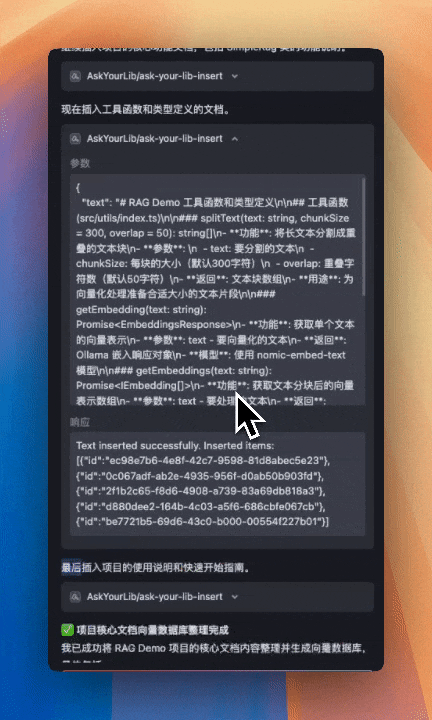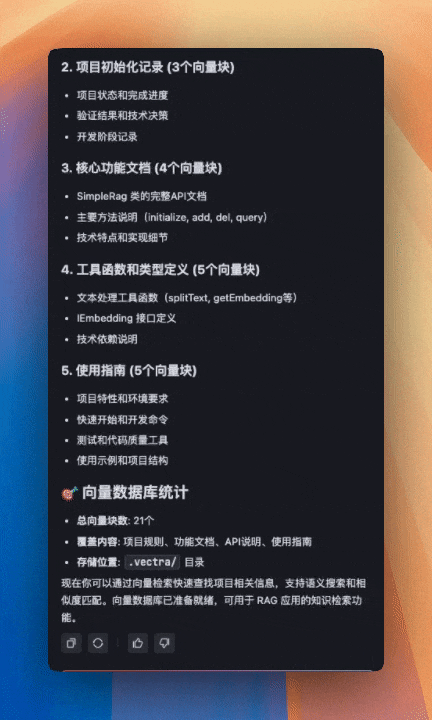
通过 ollama qwen3:1.7b 进行对话
现在有了向量数据,我们就可以对接 ollama 的 qwen3:1.7b 模型进行对话了。
在进行对话前,我们写一段代码测试一下向量数据库的效果。刚才我已经跑了一遍 MCP,生成了向量数据,现在写一个测试脚本:
examples/ask-your-lib.ts
import { SimpleRag } from '../src/index';
async function main() {
const rag = new SimpleRag();
await rag.initialize();
const question = process.argv[process.argv.length - 1];
const res = await rag.query(question);
console.log(res);
}
main();
接着我们在控制台运行命令。
npx jsx examples/ask-your-lib.ts 'RAG Demo 是做什么的?'
可以看到返回如下结果。
[
{
text: '# RAG Demo\n' +
'\n' +
'一个基于 TypeScript 的 Node.js 项目,实现了完整的 RAG(检索增强生成)功能演示。项目使用 Ollama 进行文本嵌入,Vectra 进行本地向量存储,提供了简单易用的 RAG 接口。\n' +
'\n' +
'## 🚀 核心特性\n' +
'\n' +
'### RAG 功能\n' +
'- **文本嵌入**: 基于 Ollama 的 `nomic-embed-text` 模型\n' +
'- **向量存储**: 使用 Vectra 进行本地文件系统存储\n' +
'- **智能分块**: 自动将长文本分割为可处理的块\n' +
'- **相似度检索**: 支持语义相似度查询\n' +
'- **增删改查**: 完整的向量数据库操作\n' +
'\n' +
'### 技术栈',
query: 'RAG Demo 是做什么的?',
simularity: 0.7141837723769591,
id: 'b18bac0d-404c-4e34-a992-374d817560ea'
},
{
text: 'demo/\n' +
'├── src/ # 源代码目录\n' +
'│ ├── index.ts # SimpleRag 主类实现\n' +
'│ ├── types/ # 类型定义\n' +
'│ │ └── index.ts # IEmbedding 接口定义\n' +
'│ └── utils/ # 工具函数\n' +
'│ └── index.ts # 文本分块和嵌入工具\n' +
'├── examples/ # 使用示例\n' +
'│ └── rag-usage.ts # ',
query: 'RAG Demo 是做什么的?',
simularity: 0.7123087710639455,
id: '61312a0c-a1b1-46bb-959d-cb0329ae424d'
},
{
text: '# Package.json 完整配置文档\n' +
'\n' +
'## 项目基本信息\n' +
'```json\n' +
'{\n' +
' "name": "rag_demo",\n' +
' "version": "1.0.0",\n' +
' "description": "A TypeScript Node.js project for RAG demo",\n' +
' "main": "dist/index.js",\n' +
' "types": "dist/index.d.ts",\n' +
' "author": "RAG Demo Project",\n' +
' "license": "ISC"\n' +
'}\n' +
'```\n' +
'\n' +
'## 可执行文件配置\n' +
'```json\n' +
'{\n' +
' "bin": {\n' +
' ',
query: 'RAG Demo 是做什么的?',
simularity: 0.6829199356959024,
id: '64f17ffd-b799-4491-99f9-552790590861'
},
{
text: '相似度检索**: 支持语义相似度查询\n' +
'- **增删改查**: 完整的向量数据库操作\n' +
'\n' +
'### 技术栈\n' +
'- **TypeScript**: 完整的类型支持和严格模式\n' +
'- **CommonJS**: 兼容性输出格式\n' +
'- **Jest**: 完整的单元测试框架\n' +
'- **ESLint + Prettier**: 代码质量和格式化\n' +
'- **pnpm**: 高效的包管理工具\n' +
'- **Ollama**: AI 模型推理引擎\n' +
'- **Vectra**: 本地向量数据库\n' +
'\n' +
'## 📦 项目结构\n' +
'\n' +
'```\n' +
'rag_demo/\n' +
'├── src/ # 源代码目录\n' +
'│ ├── ',
query: 'RAG Demo 是做什么的?',
simularity: 0.6614571294074207,
id: '4e088b6c-80a2-4ae2-8531-84529c99d5b8'
},
{
text: '/ # 使用示例\n' +
'│ └── rag-usage.ts # RAG 功能演示\n' +
'├── tests/ # 测试文件目录\n' +
'│ ├── index.test.ts\n' +
'│ └── utils.test.ts\n' +
'├── .trae/ # 项目配置和记忆库\n' +
'│ ├── project_rules.md # 项目开发规范\n' +
'│ └── memory_bank/ # 项目记忆存储\n' +
'├── .vectra/ # 向量数据库存储目录\n' +
'├── dist/ ',
query: 'RAG Demo 是做什么的?',
simularity: 0.6591809430168598,
id: '5ba4bcce-4cb8-4e5f-a46e-c6ea2c3df130'
}
]
现在我们接入 ollama 的 qwen3:1.7b,修改 examples/ask-your-lib.ts ,先故意不引入 RAG 搜索结果的数据:
import { SimpleRag } from '../src/index';
import ollama from 'ollama';
async function main() {
const rag = new SimpleRag();
await rag.initialize();
const question = process.argv[process.argv.length - 1];
const res = await rag.query(question);
const messages = [
{ role: 'user', content: 'RAG Demo 是做什么的?' }
];
const response = await ollama.chat({
model: 'qwen3:1.7b',
messages,
stream: true
});
for await (const part of response) {
process.stdout.write(part.message.content);
}
}
main();
这时候我们看大模型输出的结果:
RAG Demo(Retrieval-Augmented Generation Demo)是一种通过**检索外部知识**并结合**生成模型**进行问答或任务处理的演示系统。它的核心目标是通过检索知识库中的信息,增强生成模型的推理能力,从而提供更准确、更丰富的答案。
---
### **RAG Demo 的核心功能**
1. **知识检索**
- 从预定义的知识库(如文档、数据库、维基百科等)中检索与问题相关的具体信息。
- 例如:用户提问“苹果公司的创始人是谁?”,系统会检索到“乔布斯”。
2. **生成答案**
- 将检索到的信息与生成模型(如BERT、GPT等)结合,生成自然流畅的回答。
- 例如:结合“乔布斯创立了苹果公司”和“苹果公司成立于1976年”,生成“乔布斯是苹果公司的创始人,该公司成立于1976年。”
3. **动态更新**
- 支持实时更新知识库,确保答案的时效性和准确性。
---
### **RAG Demo 的典型应用场景**
1. **问答系统**
- 为用户提供基于知识库的精准问答(如法律咨询、技术问题解答)。
2. **文档处理**
- 从文档中提取关键信息并生成摘要或问答(如合同条款解析)。
3. **知识库问答**
- 通过检索和生成结合,回答复杂问题(如历史事件、科学原理等)。
4. **多语言支持**
- 支持多种语言的检索和生成,适用于国际化场景(如翻译问答、多语言客服)。
---
### **RAG Demo 的优势**
- **准确性**:通过检索最新或权威信息,避免生成错误。
- **灵活性**:可定制知识库内容,适应不同领域需求。
- **效率**:减少人工处理,提升问答效率。
---
### **注意事项**
- **依赖外部数据**:若知识库不完整或过时,可能影响回答质量。
- **复杂问题处理**:需结合多源信息和逻辑推理,避免单一检索导致的“信息孤岛”。
- **可解释性**:生成的回答需具备可解释性,便于用户验证信息来源。
---
### **示例流程**
1. **用户提问**:
“如何制作蛋糕?”
2. **检索知识库**:
- 提取“烘焙材料(面粉、鸡蛋、糖等)、步骤(混合、烘烤)、常见问题(温度控制)”等信息。
3. **生成回答**:
“制作蛋糕需准备面粉、鸡蛋、糖等材料。步骤包括:1. 将材料混合;2. 烤箱预热;3. 烘烤15-20分钟。注意温度控制在180℃左右。”
---
### **总结**
RAG Demo 是通过**检索知识增强生成能力**的实用工具,广泛应用于问答、文档处理、多语言支持等领域。它的核心价值在于结合外部信息,提升回答的准确性与实用性。
我们会看到,由于缺少必要的知识,模型给出的答案出现严重的幻觉。
现在我们加入知识库,继续修改 examples/ask-your-lib.ts :
import { SimpleRag } from '../src/index';
import ollama from 'ollama';
async function main() {
const rag = new SimpleRag();
await rag.initialize();
const question = process.argv[process.argv.length - 1];
const res = await rag.query(question);
const messages = [
{
role: 'system',
content: `You are a helpful assistant. Answer the question based on the context below. If the context does not contain the answer, say "I don't know". Do not make up an answer.\n\nContext:\n${JSON.stringify(res)}`,
},
{ role: 'user', content: 'RAG Demo 是做什么的?' }
];
const response = await ollama.chat({
model: 'qwen3:1.7b',
messages,
stream: true
});
for await (const part of response) {
process.stdout.write(part.message.content);
}
}
main();
上面的代码我们实际上就修改了一处,我们直接将向量数据库返回的结果 JSON 序列化后作为 system prompt 传入,这样大模型就可以根据这个上下文进行回答了。
这次大模型回答的结果如下。
RAG Demo 是一个基于 TypeScript 的 Node.js 项目,实现了完整的 RAG(检索增强生成)功能演示。它使用 Ollama 进行文本嵌入(如 `nomic-embed-text` 模型),并利用 Vectra 进行本地向量存储。项目支持文本分块、语义相似度检索以及向量数据库的增删改查操作,同时提供了简单易用的 RAG 接口。项目结构包含源代码、示例、测试文件以及配置文件,旨在展示 RAG 的核心特性。
这就达到了我们的期待。
修正一个细节
现在我们基本上实现了预期的功能,但是我们的 MCP 应该不仅能对于当前项目使用,对于其他项目也应该有效,但现在有个问题,那就是 SimpleRag 的 initialize 方法有个参数 indexPath,它默认是 path.join(__dirname, '..', indexPath) 。这样的话 MCP 每次生成 .vectra 都在 rag_demo 这个项目自己的目录下,显然不符合我们的要求,我们希望在别的项目使用时,生成在该项目的根目录下。
所以这里我们需要给 MCP Server 的 ask-your-lib-initialize 指定参数。
我们将 ask-youre-lib-initialize 工具修改为后面这样。
server.tool(
'ask-your-lib-initialize',
`Initialize the vector database operations and clean up any existing .vectra directory.`,
{
indexPath: z.string().describe('The path to the vector database index. If not specified by the user, defaults to the .vectra subdirectory under the current project directory.'),
},
async ({ indexPath }) => {
try {
// Check if .vectra directory exists in project root and remove it
const projectRoot = path.resolve(__dirname, '../../');
const vectraPath = path.join(projectRoot, '.vectra');
const generateMcpPrompt = await loadPrompt('generate');
try {
await fs.access(vectraPath);
await fs.rm(vectraPath, { recursive: true, force: true });
console.log('Removed existing .vectra directory');
} catch (error) {
// Directory doesn't exist, which is fine
console.log('.vectra directory does not exist, skipping removal');
}
// Create new SimpleRag instance
simpleRagInstance = new SimpleRag(indexPath);
return {
content: [{
type: 'text',
text: `⚠️ The guide to follow: \n${generateMcpPrompt}\n\n`
}],
};
} catch (error) {
console.error(`Error initializing SimpleRag: ${error}`);
return {
content: [{
type: 'text',
text: `Error initializing SimpleRag: ${error}`
}],
};
}
}
)
这里我们增加了一个 indexPath 参数,因为我们用 zod 描述了参数的元数据信息,让执行 MCP 工具的 AI Coding 大模型自己知道该用什么路径去给 indexPath 传递正确的参数。
这样我们就可以让这个 MCP 在其他项目中正确构建向量数据了。
要点总结
这一讲,我们通过 AI Coding 工具的大模型,将项目文档摘要整理,构建向量数据库,然后通过 ollama 的本地大模型进行对话。
我们可以清楚地看到,经过 RAG 和没经过 RAG 的时候,大模型对问题的回答有很大的差别。对于特定知识的问题,我们通过 RAG 解决了大模型回答不出或者出现幻觉的问题。
所以 RAG 技术对于企业本地部署的 AI 应用有着非常重要的作用,我们作为开发者应该掌握其核心原理。
这两节课我们所实践的内容还比较简陋,实际用起来肯定还有很多细节问题有待完善,这些问题我就留在课后练习中,希望有兴趣的同学能够动手进一步深入研究。
课后练习
我们在实际使用过程中,发现对于一些复杂的库,大模型输出的向量数据不够,还是比较简陋,这应该是 generate.md 提示词的问题。你可以试着改写提示词,增加更明确的指示和步骤,让大模型能做得更好,生成更详尽的内容。
我们课程中的例子,检索内容和对话是通过 ollama 本地大模型完成的,事实上我们同样也可以增加 MCP 工具,让 AI Coding 的智能体通过 MCP 读取项目信息后进行回答。
实际上这也很实用,因为我们虽然能够在 AI Coding 中基于当前项目上下文与智能体对话,但我们不能让智能体默认获取我们安装于 node_modules 下的依赖模块的上下文。这时候如果我们发现有项目有生成 .vectra 向量数据库,我们就可以让智能体直接通过这个 MCP 工具获取内容,然后就可以拿到这个项目最新的第一手资料,这对 AI 运用这个项目生成代码很有帮助。
这也正好解决一个非常普遍的问题,即 AI Coding 时,有的依赖库 API 版本已经更新,但 AI 还是用老版本 API 导致代码出 bug 的问题。你可以尝试实现让 AI Coding 智能体通过查找依赖包内的 .vectra 了解最新 API 的功能吗?将你的尝试方法和心得体会分享到评论区吧!
这节课的完整代码详见 GitHub 仓库。
精选留言
2025-07-31 05:06:05
2025-07-31 04:12:54